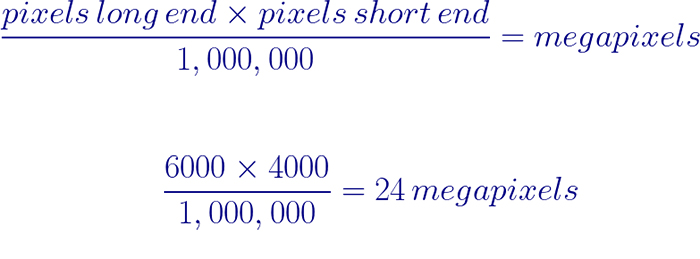This article will take a deep look at how many megapixels are good for a camera and how many pixels you really need…
Photos are made up of tiny square pixels. Each pixel contains color information, and millions of them combine to form a unique pattern. Step back, and your eyes see the dots of color and light as an image.
In many ways, photos are like a tiled mosaic. The more pixels there are, the smaller the little squares that make up our image. So the transitions between colors and shapes are more gradual, and the edges can be sharper.
On the face of it, more megapixels seem like a good idea. Plus, camera manufacturers’ hype around megapixels reinforces this idea. But it is not always the case that more pixels are better.

How Many Megapixels is Good for a Camera?
The answer to this question depends on what you’re using your camera for. On average, a 20-megapixel camera is adequate for most printing needs. You need even less for sharing photos online. But professional photographers who print at a large scale or need to crop images may need cameras with more megapixels.
First, let’s look at what megapixels are and how many megapixels are in our cameras. Then we’ll look at how many pixels you really need in different scenarios.
What Are Megapixels?
Megapixels are millions of tiny pixels. One megapixel (MP) is one million pixels. So a one-megapixel camera has a million individual pixels on the sensor collecting light. This sounds like a lot. But today’s digital cameras record 10, 20, or even 100 million pixels for each image.
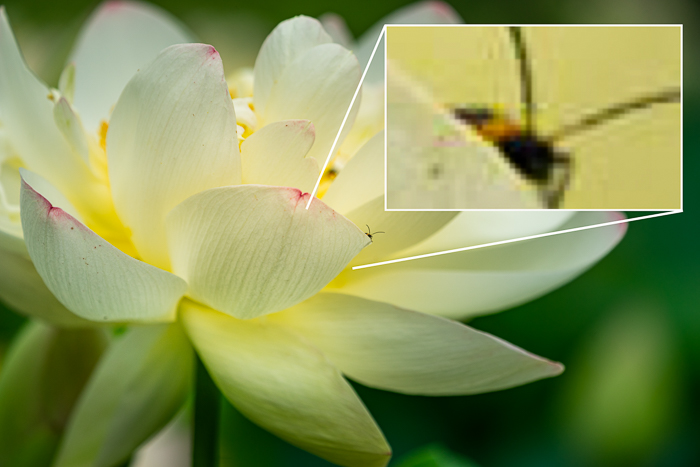
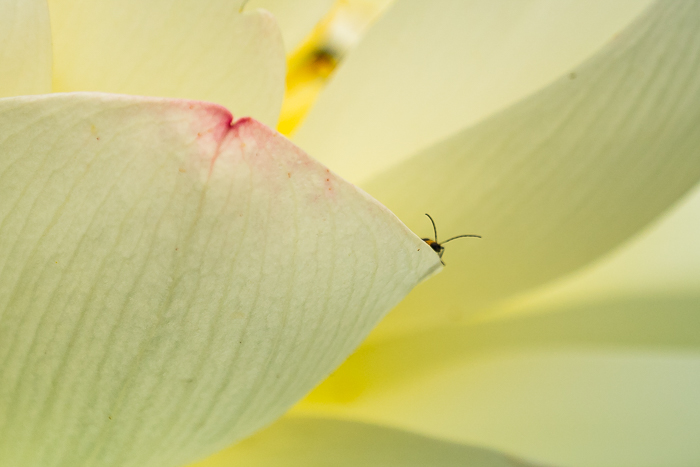
Your eyes make sense of all the little dots at a normal viewing distance, resolving the dots into an image. In most cases, we do not see the individual pixels. But when we can see the squares in the form of a rough edge, we call this pixelation.
In the zoomed-in box of this image, we see the grid work that makes up the photo. It is a 24-megapixel image zoomed in 1600%. But zoomed out to normal view, the edges look smooth.
What is Resolution? (And How Do I Calculate Megapixels?)
Resolution describes the megapixel count in a photo. A high-resolution image has a lot of pixels. A low-resolution image has fewer pixels. There is no hard-and-fast definition of “high” or “low” pixel resolution. It is more of a comparison.
Camera manufacturers advertise how many megapixels are on their cameras. But you can easily figure it out by looking at the size of your image.
A 24-megapixel image measures 6000 pixels on the long side by 4000 pixels on the short side (6000x4000px). Multiply 6000 by 4000, and you get the total number of pixels in your image. In this case, 24 million (24,000,000). Divide that by 1 million (1,000,000), and you have 24 megapixels.
How Many Megapixels Does a Camera Sensor Have?
Most cameras sensors fall into the 18-24MP range. But with each generation of cameras, engineers seem to find a way of packing more pixels on a sensor. Since the first digital camera release, manufacturers have steadily increased the megapixel count on the cameras’ sensors.
In 1994, Apple released the first mainstream digital camera, the Apple Quicktake 100. The image sensor had 0.3 megapixels or just over 300,000 pixels. The images had a resolution of 640×480 pixels.
Which Camera Has the Most Megapixels?
Currently, cameras with the most megapixels use large, medium format sensors. The Phase One XF IQ4 camera has 151MP. Of the cameras that use full-frame sensors, The Sony a7R IV has the most megapixels with 61MP. Each photo has a resolution of 9504×6336 pixels.
Publicity surrounding each new camera release looks like a race to add as many megapixels as possible. But these cameras are at the extreme end of the megapixel range. The Sony a7 RIV can create an image of 240 megapixels. The Hasselblad H6D-400C Multi-Shot can create a 400-megapixel image.
But in 2020, Sony released the a7S III. This camera has only 12MP, the fewest of any professional-level camera on the market. Sony released this camera after the 61MP a7R IV.
So, Sony could make a camera with a higher resolution but chose not to. That tells us that more megapixels are not always better. Let’s look at why.
How Does Pixel Size Affect Image Quality?
Pixels are not all the same size. Sensors are different sizes, and so are the pixels that collect light. For instance, a crop sensor is about half as large (48%) as a full-frame sensor on a mirrorless or DSLR camera.
So, even though both a crop sensor and a full-frame sensor have 24 million pixels, the pixels are not the same size. Each pixel on the crop sensor is smaller than a pixel on a full-frame sensor.
The bigger pixels on the full-frame camera collect more light. You can think of pixels on a sensor as a series of buckets. Light fills up the pixels like rainwater fills a bucket. The larger the buckets, the more water they can hold. In digital photography, this means cleaner images in low-light situations.
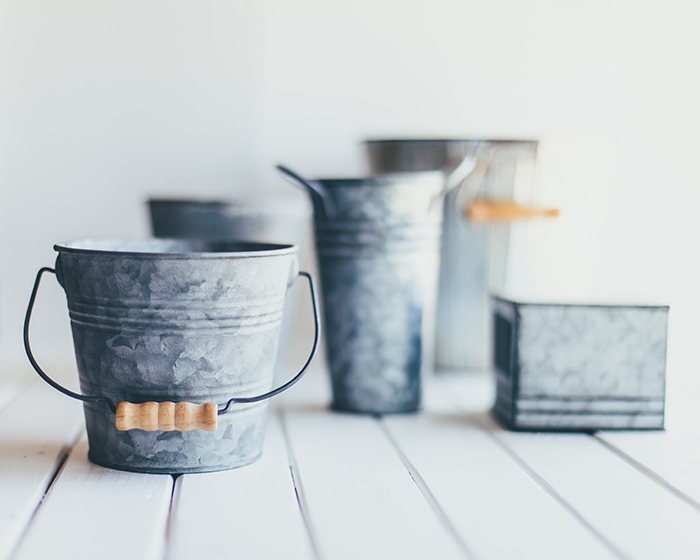

On the other hand, smaller pixels often result in noisier images. This is not so much of an issue now with improvements to ISO performance. But you may not be able to set your ISO as high on a 24-megapixel crop sensor camera as you might on a full-frame sensor with the same number of pixels.
Sony’s a7S III has only 12MP on a full-frame sensor. That means each pixel is larger than the pixels on the higher resolution 61MP a7R IV. They collect more light with less noise.
We use the term high-resolution when talking about cameras with a lot of megapixels. So It is easy to think that megapixels are the only factor influencing image quality. But that is not the case. Other features of digital cameras affect the sharpness of the photo. These include the quality of the image processor and lens quality.
How Many Megapixels Does a Camera Need?
In truth, all digital SLR cameras you buy today, including smartphone cameras, have enough pixels for the average user. Our eyes will see the photos produced as a clear image.
But, yes, the more pixels there are on a sensor, the more gradual the colors and shapes change. So there are situations where you want to use high megapixel cameras. But you have to zoom in a lot to see the edges of a pixel in your image.
How Many Megapixels Do I Really Need?
Let’s explore different situations to see if extra megapixels are needed or if there is a time for too many megapixels.
How Many Megapixels Do You Need to Crop?
The more megapixels you have, the better your ability to zoom in and crop an image. When you crop in on a picture, you throw away some of the pixels on the edge of the frame. The more megapixels you have to work with, the more you can crop out and still have high-resolution images.
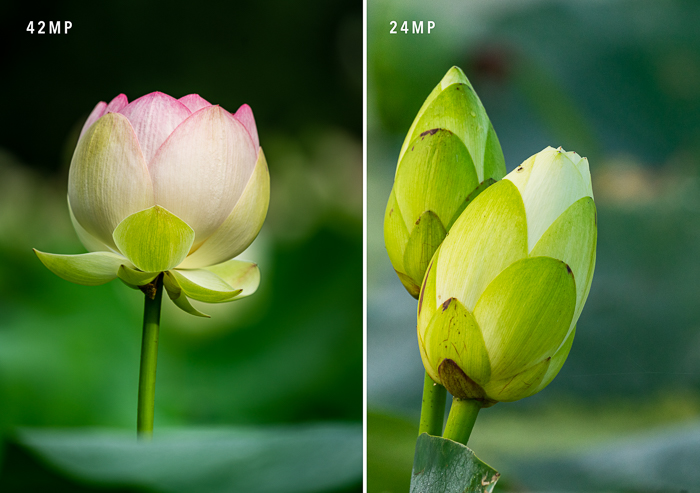
Many photographers like to frame the scene in camera exactly the way they want to see the final image. But that is not always possible. You may want to crop and fill the frame with your subject.
The original file of this flower image was 42MP. A tight crop reduced the file to under 10MP.
How Many Megapixels Do You Need for Printing?
The number of megapixels you need for printing depends on how large you want to print your photo. If you make a small, postcard-sized print, your image only needs to be about 2MP. More megapixels only really come into play when you are making large prints.
Resolution limits how large you can print good-quality images. You can only print a 1080x1080pix Instagram image at about 10×10″ before the quality deteriorates. Many print companies have print-size calculators that help you find the best print size to print.
A high megapixel camera with 100MP is marketed to photographers making large advertising prints. But what about those large billboards printed from iPhone photos? The current iPhone only has 12 megapixels. This should limit the print size to about 24” on the long side.
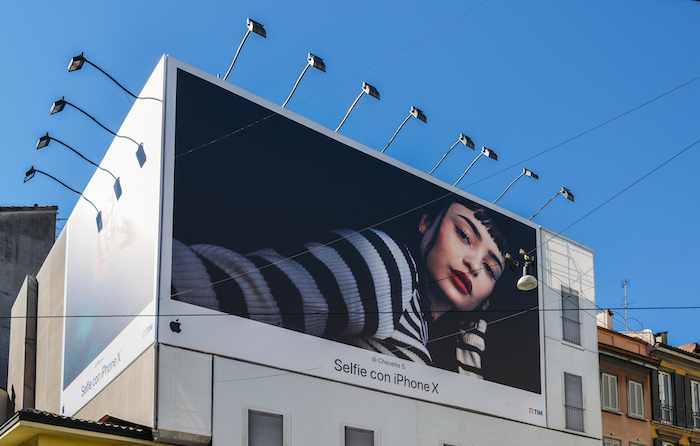

You can see the pixelation if you get close to one of these iPhone billboard ads. But no one views billboards from close-up. They are designed to be viewed from afar. Our eyes resolve the image, and we see the shapes clearly.
If you want to make large high-resolution prints, you need a camera with a lot of megapixels. Or do you? Let’s look at ways to increase resolution in post-processing.
How Can You Increase Image Quality in Post-Processing?
You can now simulate a higher resolution with image editing software. For instance, Adobe Photoshop’s Superzoom neural filter lets you crop in but retain all the pixels. ON1 has a similar program called Resize AI. And Topaz has Gigapixel AI. These programs allow you to enlarge photos while keeping detail and sharpness.
This image started as a 24-megapixel file. But a severe crop reduced the file to about 2 megapixels. This reduces printing size to about 6×4″ before quality becomes a factor. Using Photoshop’s Superzoom neural filter, I can crop in and keep all 24 megapixels.
With these post-processing programs, you can take an image with a 12MP iPhone and enlarge it in post-processing.
How Many Megapixels Do You Need for Video?
The current standard for mass-market video is 4K resolution. This is 3840×2160 pixels. So to produce a 4K video, you only need just over 8MP on a camera. Adding megapixels is not going to get you a better video. In fact, extra pixels only collect extra light in the form of noise. Sony designed the a7S III for low-light photography and video production with this in mind.
How Many Megapixels Do You Need for Social Media?
The number of pixels you need for social media has a lot to do with how you want to share images. Most digital photographers tend to share pictures on social media platforms or websites. On many social media platforms, there is an image resolution limit.
For instance, on Instagram, it does not matter how many pixels your image has when you upload it. The maximum resolution is 1080×1350 pixels or about 1.5MP. This is partially to reduce the size of the files. Millions of photos are uploaded each day and stored on the Instagram servers.
How Many Megapixels Do You Need for Viewing on Screens?
There is also a limit to how much resolution we can see on phone or computer. There is no need to upload larger images since the most common screen resolution is 1920×1080. This equates to just over 2MP. We cannot view higher resolution images on most computer screens.
For instance, you will not notice a difference in image resolution in this article. Website content often limits image file size to speed the loading of webpages (we standardize all images at 700 pixels on the long end).
How Many Megapixels Do Smartphone Cameras Have?
The first cell phone cameras had less than 1MP. The iPhone 13 has 12MP packed onto a tiny sensor about 1/6th the size of a full-frame sensor. You can follow the same guidelines for regular cameras when deciding how many megapixels is good for a phone camera.
Recently, camera manufacturers have begun incorporating pixel shift technology into high-end cameras. This technology increases the megapixel count and lets you take ultra-high-resolution images.
With pixel shift, the camera takes several pictures and stitches them together. It is similar to HDR bracketing. But instead of changing exposures, the camera shifts the sensor a little each time.
How Many Megapixels is Good for a Camera?
It may seem that camera companies continue to add more megapixels to each generation of mirrorless, DSLR, and phone cameras. But there seems to be a sweet spot around 20 megapixels. These files are large enough to print for most situations. For photographers sharing images online, there is no need for even this many pixels.
Photographers who shoot video or photographs in low-light situations need fewer megapixels. Photographers who print large or need to crop tightly into the frame are the ones who benefit most from buying high-resolution cameras.
Knowing how many megapixels you really need can save you hundreds or thousands of dollars on your next camera. Almost every camera on the market, including phone cameras, have enough megapixels for most photographers’ needs. When deciding on your next camera, you can use other factors to select one.
Check out the highest megapixel cameras in our camera database, or compare two high megapixel cameras in our comparison tool next!